Social Lobby Map applies a structured, data-driven methodology to track how companies shape labour and human rights regulations.
Our framework provides clear evidence of corporate influence, helping stakeholders evaluate lobbying behaviour and advocate for stronger protections.

Corporate lobbying is one of the most powerful tools companies use to shape the regulatory environment. While many businesses publicly commit to respecting human rights and sustainability, their lobbying activities often tell a different story. By analysing corporate lobbying on human rights, Social LobbyMap research and data helps uncover:

We monitor:

Open Methodology: our scoring and assessment criteria are publicly available to ensure transparency.
Continuous Improvement: we reviewed and refined our methodology in response to stakeholder feedback and evolving policy landscapes and we will repeat this process periodically.
Collaboration with Experts: we work with human rights experts, labor organisations, and ESG researchers to validate and strengthen our approach.

We currently analyse 160 influential actors, examining their approaches to corporate lobbying on human rights, including:
Our coverage will expand as the project proceeds and new policy areas emerge.
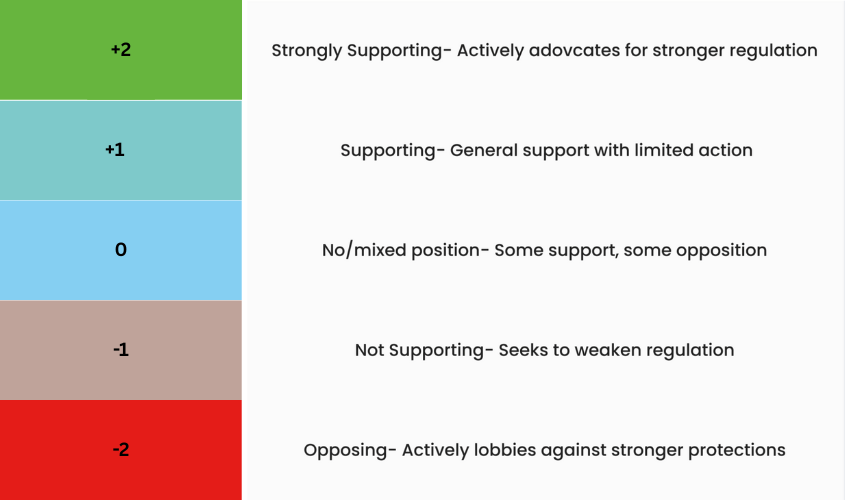
We assign scores for an organisation’s approach to corporate lobbying on human rights on a 5-point scale:
We assess corporate lobbying using nine key indicators aligned with international frameworks such as the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights and ILO core labour standards. These indicators allow us to evaluate how companies and trade associations influence policies that affect people, workers, communities, and supply chains.
We assess businesses’ positions on policies that regulate how they:
Identify, prevent, and address human rights risks in their operations.
Provide or cooperate in effective remedies when rights are violated.
Monitor and manage human rights risks across their entire value chain, including suppliers.
Involve stakeholders in shaping policies and addressing risks.
Ensure that workers can organise, join unions and negotiate collectively – free from retaliation.
Prevent forced labour, including modern slavery and human trafficking.
Prevent child labour across operations and supply chains.
Implement workplace policies that promote equality and prohibit discrimination.
Maintain safe and healthy working conditions, mitigating risks to workers.